Understanding the basics of soft forks and hard forks of Ethereum
In terms of cryptocurrency, understanding the difference between soft forks and hard forks is crucial to those interested in participating in the blockchain revolution. This article discusses what a soft fork, the hard fork and its differences is.
Fork Soft: a flexible option
Soft Fork is an alternative approach to the Ethereum network to implement changes that allow incremental updates without interfering throughout the ecosystem. Unlike traditional hard forks that require most users unanimous votes, soft forks can be implemented with less risk of fanfare and less safety risks.
Imagine a soft fork as a gradual update for the operating system for smartphones. You don’t have to move to a fully new application or hardware, but install an incremental update that improves performance or increases new features over time. Similarly, a soft fork allows developers to test and duct changes in the Ethereum network without causing great reform.
The main features of the soft fork:
- Additional Updates : Changes are made at small intervals, which facilitates users’ testing and adjustment before all implementation.
- Less risk of catastrophic defect : As the update is gradual, there is less likely to cause significant disadvantages or network interference.
- Community Participation
: Developers can participate in the Soft Fork process through an open source participation and testing, allowing them to identify possible problems and improve the overall quality of the update.
HARD FORK: Traditional approach
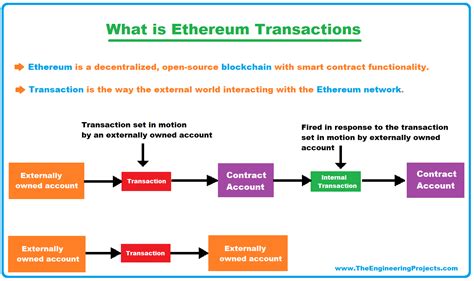
On the other hand, a hard fork is a more dramatic change that requires consensus from all users before being implemented. It’s like updating your smartphone without installing new apps – you need to move to a completely different operating system or hardware.
Unlike soft forks, hard forks are usually used for main updates or significant changes that cannot be reversed rapidly if problems occur during the implementation process. Hard forks usually contain a more complex and controversial process as they require a vote based on consensus on all users, which can lead to disagreement and delays.
Main features of the hard fork:
- Consensus based : Changes are implemented through a voting process that requires the majority of the user contract.
- Catastropic failure risk : Hard forks carry significant risk of disturbing the network or causing financial losses to users who have funds in other wallets or stock exchanges.
- Limited Community Participation *: Developers may not have much entrance during the hard fork development phase and it may be more difficult to test and adapt before implementation.
When can a soft fork be implemented?
Although a soft fork can be implemented by a special rule, it usually occurs in situations where:
- Additional updates are essential : Changes that increase new features or improve performance without disturbing the network.
- Community participation is crucial : Developers want to test and refine changes before implementation, ensuring that they meet community expectations.
- The risk of a catastrophic defect is low : the change has no significant effects on users if problems occur during the test.
In short, soft forks provide a more flexible and incremental approach to implement changes in the Ethereum network, while hard forks represent a traditional approach that requires consensus and may be more challenging to implement. Understanding these differences will help you sail the development of cryptocurrency in a complex world and make conscious decisions about participation in the blockchain revolution.
 VN
VN